Cryptography and computer security compose the perfect key to lock and unlock your digital environments. Although each of them emerged and evolved autonomously to conquer their own places of honor; cryptography and computer security embed to guarantee exclusive access only to those who you authorize.
Cryptography and computer security compose the perfect key to lock and unlock your digital environments. Although each of them emerged and evolved autonomously to conquer their own places of honor; cryptography and computer security embed to guarantee exclusive access only to those who you authorize.
As such, cryptography and computer security feed and complement each other to enhance the security of your digital environments. Also, they give everyone the opportunity to protect their sensitive data from all kind of virtual threats. In short, cryptography and computer security are a fundamental part of the data integrity and its preservation.
However, is cryptography enough to guarantee the data protection, and ensure the privacy of the interactions in the digital environments? What secrets hide behind our keys and passwords? How did cryptography and computer security meet and embed to enhance digital security? Let’s see their evolution.
Cryptography and computer security: Some interesting facts
Although cryptography accumulates thousands of years of history; it started with the simple desire to hide or restrict important messages to only a few.
A man is master of his silence and a slave of his words
The basis of cryptography took root in this premise and from it; countless techniques popped up to guarantee the integrity of the information we reveal, and segregate it from the information we want to keep in secret.
 It is worth to mention the famous case of the Enigma machine; the way the Allies managed to break its code; and its repercussions over the end of World War II. Now, if this was possible in the first half of the past century, can we even imagine the evolution and repercussion of a similar event in today’s computer science?
It is worth to mention the famous case of the Enigma machine; the way the Allies managed to break its code; and its repercussions over the end of World War II. Now, if this was possible in the first half of the past century, can we even imagine the evolution and repercussion of a similar event in today’s computer science?
As such, cryptography is an art of complex technique used for the protection or concealment of information. In modern times and specifically during the last century; it was mainly used to protect data and source documents with military plans and information, or containing political issues.
However, with the arrival and massification of the Internet, cryptography and computer security evolved jointly and naturally towards private industries. And from there, to individuals.
For this reason, cryptography and computer security in our time translate into various types and presentations that we better know well.
Types of cryptography and computer security we use today
Symmetric cryptography
On the one hand, we find symmetric cryptography. It employs a unique key between Sender and Recipient. That is to say; both ends of the communication know in advance the password because it has been previously shared through means without filters or protocols, as for example, a phone call; a mail; a piece of paper; etc.
It is at this point precisely where we find its greatest vulnerability: As the means sends the key in the same way as it is received; it is very easy to intercept the key or password and discover all its components without breaking the code: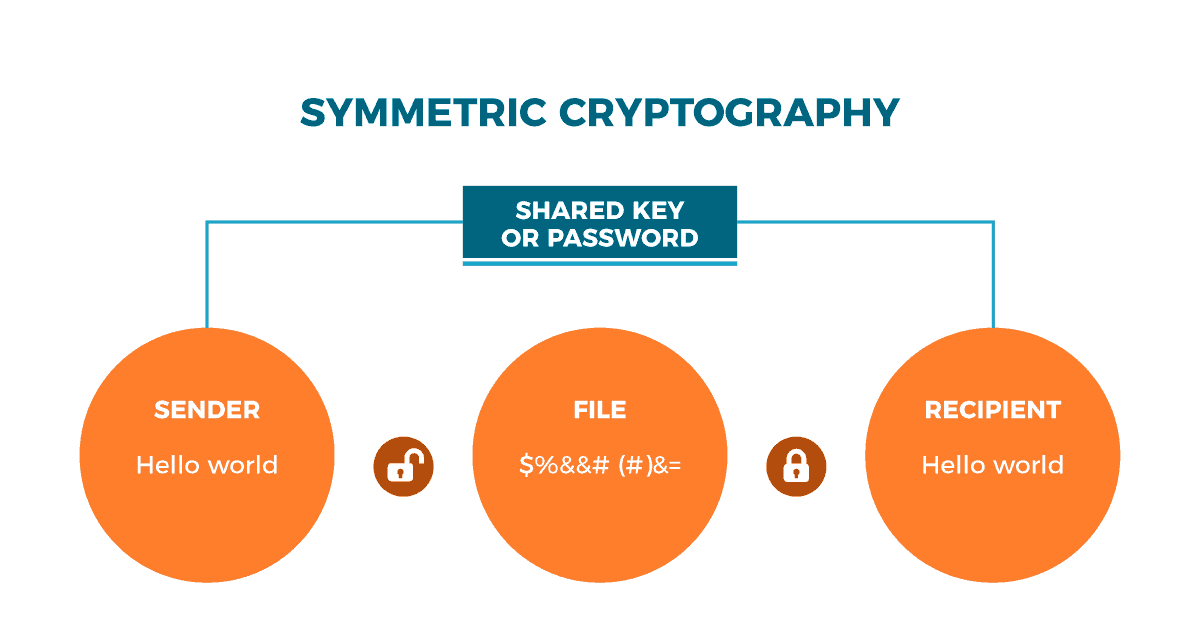
The main advantage of symmetric cryptography is its speed. Symmetric cryptography establishes and delivers messages faster; however, its lack of protection makes it extreme vulnerable and not reliable or advisable if our objective is protecting and making the information we share private.
Asymmetric cryptography
On the other hand, asymmetric cryptography employs two keys to cypher the message so to make it unintelligible. One of them is public and therefore, it does not offer any protection. The reason why this public key does not offer any protection; is because it only works as a means – or container – to send – or deliver – the message.
Diametrically opposed, the other key is private and it’s responsible for encrypting the message to keep it inintelligible to everybody but the key’s owner, and those who the owner decides to disclose it:
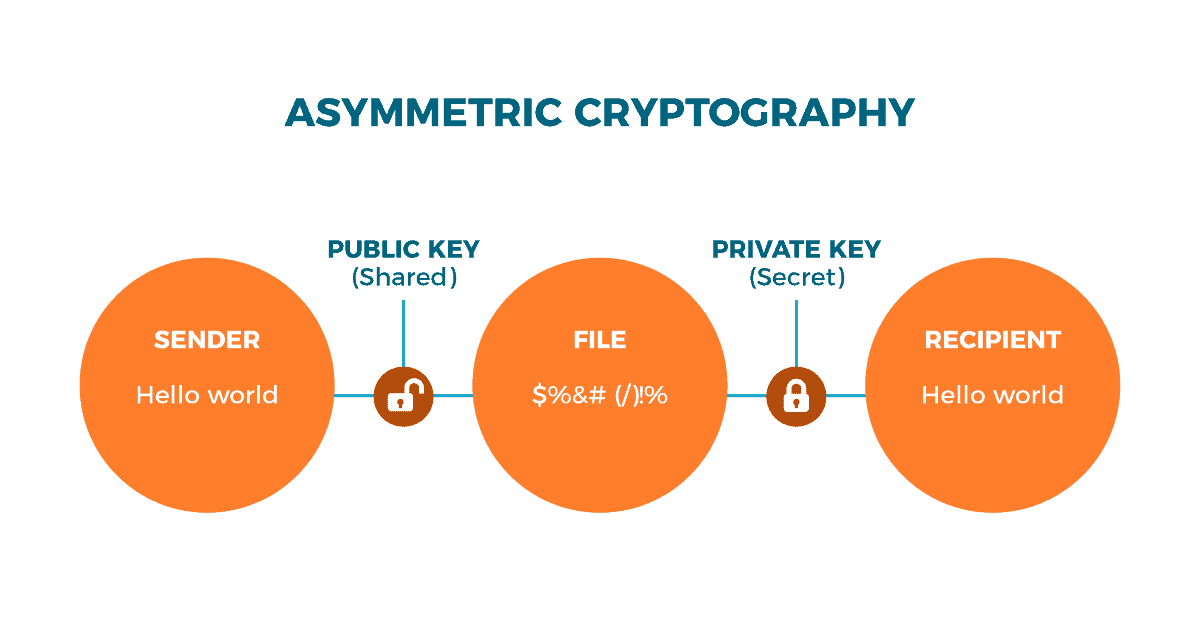
The main strength of asymmetric keys is the length of the encryption code, which with no problem can reach 2048 bits. And with each bit, it becomes more and more difficult to even try to break the code.
However, decoding asymmetric keys takes time and that’s its main disadvantage. And of course, decoding double-key encryption codes makes it even slower if you want to use a bidirectional means to exchange and interchange private information.
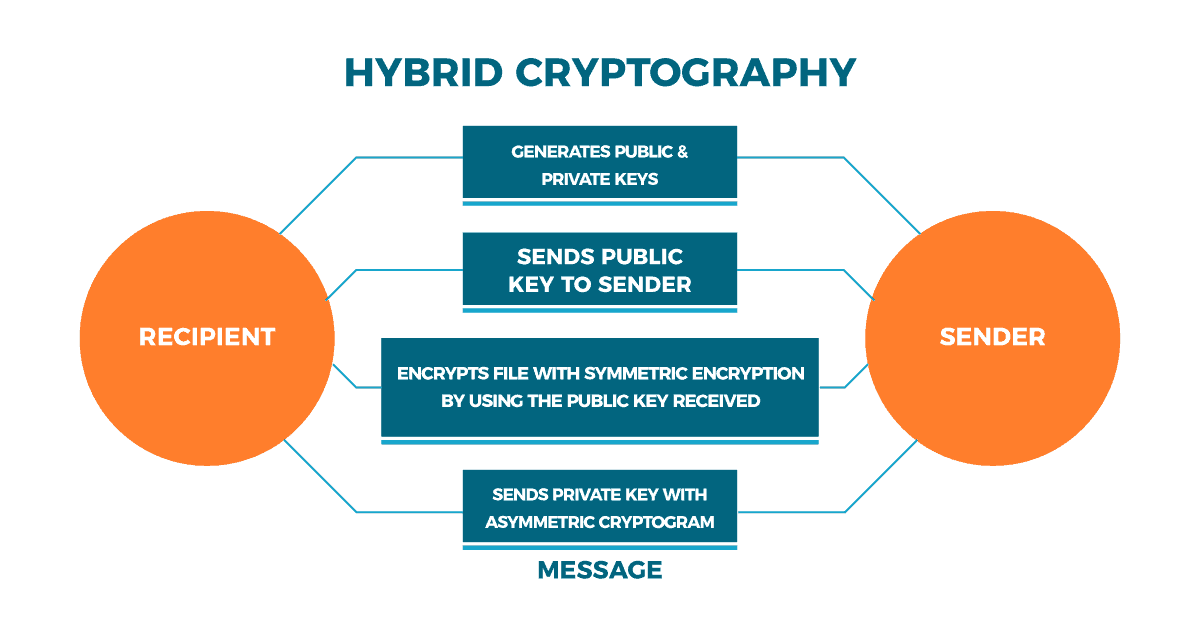
Hybrid cryptography
Last, we find hybrid cryptography. It rescues the best of the previous two to minimize their disadvantages to acceptable levels. Hybrid cryptography goes like this:
Cryptography and computer security: The Life Cycle of your Keys and Passwords
As one image reveals more than a thousand words, let’s use one to describe the life cycle of keys and passwords:
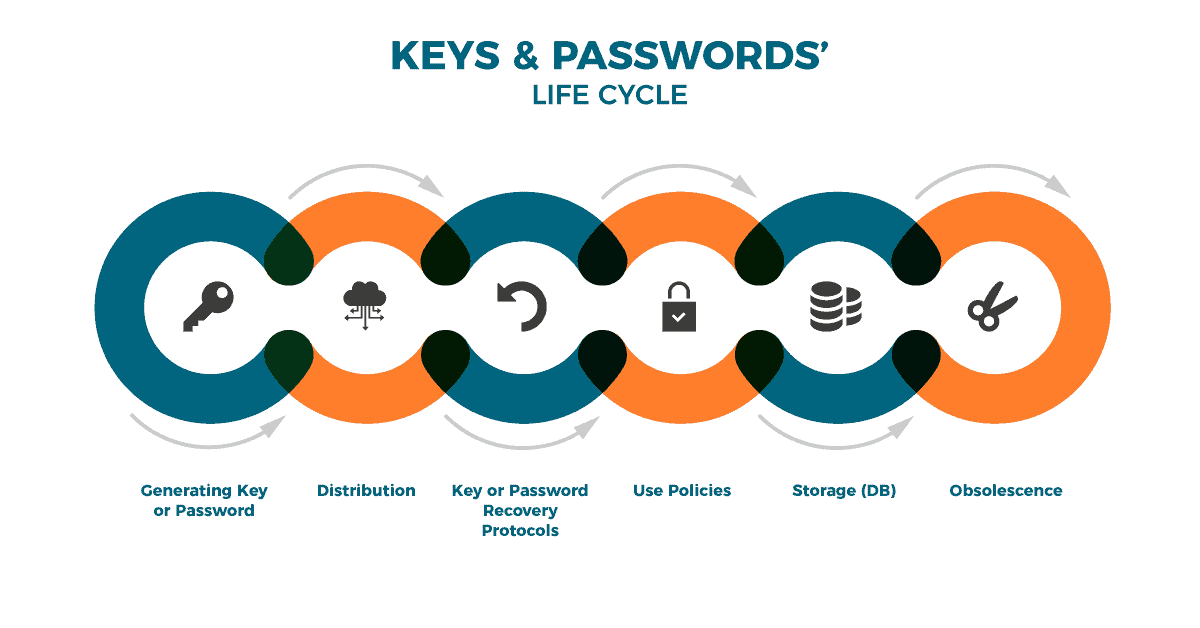
However useful, let’s go deeper in this image.
Generating keys or passwords
This action starts the life cycle of keys or passwords. The ideal is establishing protocols to generate secure keys and passwords. Here some tips:
- Employ a mixture of symbols and characters without logical coherence
- Help with mnemonics and mental images known only by whoever establishes the secure password
- Avoid using personal information such as your own birth date and similar
Distribution
Second, we find key distribution. It comprehends the way how keys or password passes to and gets its authentication in the database (DB), authorizing the access to the platform for which we have created such key or password. Distribution can be done by:
-
Manual distribution
The encrypted key is sent through different means, for example: Certified letter + telephone + fax; Injection of keys.
-
Central distribution
The parties interested in the data secure exchange establish a connection encrypted by a third party. This third party delivers secure environments to deliver encrypted communication keys to both ends.
-
Certified distribution by:
- Key transfer. The Sender generates an asymmetric key with the public key of the Receiver (asymmetric cryptography)
- Exchange or key agreement. know the key or password in advance (symmetric cryptography)
Both options are under the policies and conditions for managing keys and passwords; and they are responsible for verifying the authenticity of the data provided when establishing the password.
Password Recovery Protocol
Third, we have password recovery protocols. We activate this mechanism when we forget the key or password that we generate. In principle, there are two options that triggers this the password recovery protocol:
- Key or Password Recovery
- Reset Password or Password
Both options are subjected to the Policies and Conditions of Key or Password Management established by the owner of the application or service. They are responsible for verifying the authenticity of the data provided when generating the key or password.
Use Policies
 Fourth, Use Policies handles all considerations to generate, use, recover, replace and disposal of keys and passwords and passwords. Use Policies determine limits of use and this includes allowed characters; length of password; storage policies – in DB-; password recovery policies; and disposal of key or password for expiration or discontinuation.
Fourth, Use Policies handles all considerations to generate, use, recover, replace and disposal of keys and passwords and passwords. Use Policies determine limits of use and this includes allowed characters; length of password; storage policies – in DB-; password recovery policies; and disposal of key or password for expiration or discontinuation.
Storage in DB
In order to authenticate users and matching data with keys or passwords, the system’s owner must store all the related information in a Database; and restrict the access to it. Such restriction is based on the following security controls:
- Encryption of files containing the keys or passwords.
- Activating the access control to the DB Operating System (OS).
- Storage of cryptographic hashes for unidirectional keys and passwords instead of saving keys and passwords as such.
- Verification of host elements (host security capabilities, threats, authentication requirements).
Obsolescence
Last, we find the final stage of the life cycle of keys and passwords. It includes policies for the final disposal of keys or passwords when they reach their end of life (EOL). Remember: One of the main premises to avoid their interception; theft or disclosure is that keys and passwords aren’t meant to be used indefinitely.
In any case, there are two types of keys and passwords available once they become obsolete:
-
Disposal for Key Expiration
Keys or password maximum lifetime is established in Use Policies. This gives a predetermined time window for them to reach their EOL, so users need to create a new key or password for secure access.
-
Disposal for Key Revocation
 It occurs when the System Manager detects corruption or compromise in the keys or passwords, and in order to ensure the integrity of the data, proceeds to their immediate discontinuation. Keys or passwords can also be revoked due to force majeure (user’s resignation or death, redefinition of user privileges, updates, restructuring, etc.)
It occurs when the System Manager detects corruption or compromise in the keys or passwords, and in order to ensure the integrity of the data, proceeds to their immediate discontinuation. Keys or passwords can also be revoked due to force majeure (user’s resignation or death, redefinition of user privileges, updates, restructuring, etc.)
When keys and passwords become obsolete, their storage also become redundant. In the same way as the Use Policies determine their generation parameters; they determine the parameters for their destruction and final disposal. Generally, such controls are the following:
- Crypto-Shredding
- Secure erasing
- Physical destruction by demagnetization or crushing the magnetic medias.
- Content disclosure
Cryptography and Computer Security: The life cycle of keys & passwords and their relationship with your protection
Cryptography and the life cycle of keys and passwords are part of your IT security. Computer security comprehends both elements as it ensures the protection of your sensitive data in face off with system threats and vulnerabilities; and its fundamental reason is to shield them against any interference during the cycle:
Computer security includes the encryption of sensitive data; tokenization; and good practices for the management of the life cycle of key and passwords that protect your platforms; assets; goods and services.
As we understand how difficult it can be to process and obtain secure keys and passwords to achieve the comprehensive protection you need; we put at your disposal management tools that makes simpler for you.
Remember: If your access codes fall into the wrong hands, you put at risk all your sensitive data (personal information; financial resources; professional secrets). Take the time to generate strong passwords and strengthen your computer security. But if time is the least you have, don’t worry: You are in the right place!
As experts in comprehensive security, cryptography and computer security are two elements we pride ourselves in counting among our services. We help you create solid keys, password and private means to open your digital environments only to whoever you decide to reward with such privilege.